Jens Kamenik explains the evolution of KNX RF into KNX RF Multi, what products are available and how they are typically used.
Traditional KNX installations have relied on twisted-pair (TP) cable for communication with KNX devices and powering them. This method is simple, reliable and robust. There are, however, situations where no cable, or at least no KNX cable, is available. This might be in retrofit projects or locations where it is not possible to lay cables. In such cases, wireless KNX devices are the ideal solution.
Today, KNX supports a choice of media types, namely TP, IP and RF (Radio Frequency). Whilst KNX RF Ready has been on the market for some years now, the new KNX RF Multi standard enhances the RF capabilities of KNX through improved reliability and reduced power consumption.

The evolution of KNX RF
The technical capabilities of KNX RF have been improved with each generation; enhancing reliability and energy efficiency each time. KNX RF evolved from KNX RF 1.1. Then came KNX RF Ready, followed by KNX RF Multi and now KNX RF Multi SLE.
KNX RF Ready uses one channel and does not acknowledge transmissions. KNX RF Multi increased the reliability of KNX RF by introducing acknowledged transmissions (so-called Fast Acks), like those we are used to with KNX TP. KNX RF Multi also uses multiple channels that allow hopping to a different channel if the current channel is blocked by a non-KNX device. These new channels are called Fast channels and Slow/SLE channels. They differ in terms of bandwidth and frequencies.
The Fast channel is designed for permanently-powered devices, whereas the Slow/SLE channel is optimised for today’s battery-powered devices such as battery-driven heating actuators. In order to satisfy customer expectations, the battery should last for at least two heating seasons.
KNX RF products
In terms of KNX RF products, examples include KNX RF Multi USB interfaces for accessing the bus from a PC, and KNX RF Multi media couplers for the combination of KNX TP installations and end devices such as the battery-driven KNX RF Multi SLE heating actuator or KNX RF Multi switching units. In addition, retransmitters are available for extending the range of an RF installation.

Typical uses
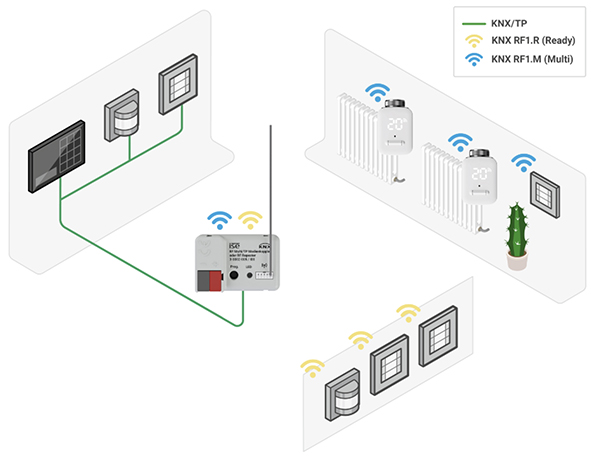
KNX RF is often used when there is a planned or existing KNX TP installation that has to be extended using KNX RF Multi devices. In such installations, the KNX RF Multi media coupler has the task of translating between physical TP and wireless RF media. Furthermore, the media coupler can translate between devices supporting KNX Secure and KNX Classic, as it is normal for KNX RF devices to support KNX Secure (since RF is an open medium), whereas TP devices may still be used without KNX Secure.
The KNX RF Multi switching unit is usually deployed with existing light switches in order to integrate them into a KNX system, and the KNX RF Multi SLE heating actuator is used to equip heating with central control via KNX.
Interoperability
Assuming an existing KNX TP installation has to be extended using RF Multi devices, the KNX RF Multi media coupler will link the TP side with the RF devices. Because the media coupler is mains-powered, it will be a Fast receiver on the RF side. Nevertheless, it has to be able to send Fast/Ready and SLE telegrams in order to incorporate battery-driven devices as well as mains-powered actuators and sensors. In other words, the new media coupler guarantees not only interoperability between KNX TP and RF, but also between the different RF modes, namely Ready, Fast and SLE. All KNX RF devices which are already installed can therefore be used with the new KNX RF Multi devices.
Summary
All situations in which no KNX cable is available, e.g., retrofitting, will benefit from KNX RF. KNX RF Multi is the ideal choice if reliability is important, and KNX RF Multi SLE is currently the only way to efficiently run battery-powered KNX RF Multi devices. Indeed the demand for reliability, data security and energy efficiency will see a growing number of KNX RF Multi products and applications coming to market, and these will likely include more battery-powered KNX RF devices such as smoke detectors, heating actuators and motion detectors.
Jens Kamenik is the RF Development Lead for ise Individuelle Software und Elektronik GmbH, developer of smart devices and remote access solutions for KNX.












